The time rate of change of a quantity such as temperature or velocity of a
material particle is known as a material derivative, and is
denoted by a superimposed dot or by 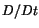 .
.
- (i)
- When referential or Lagrangian description of a
quantity is used, i.e.,
then
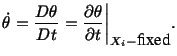 |
(3.5.1) |
- (ii)
- When spatial or Eulerian description of a
quantity is used, i.e.,
where
then
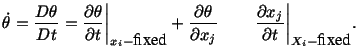 |
(3.5.2) |
In rectangular Cartesian coordinates
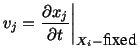 |
(3.5.3) |
is the 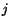 th component of the velocity of a material
particle. Therefore, in rectangular Cartesian coordinates,
th component of the velocity of a material
particle. Therefore, in rectangular Cartesian coordinates,
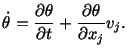 |
(3.5.4) |
Note that in (3.5.4) 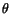 is given in the spatial description.
is given in the spatial description.
Example: Given the motion
find the spatial description of the velocity field.
Solution
Example: Given
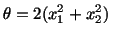 where where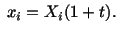 |
|
Find, at 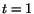 , the rate of change of temperature of the
material particle which in the reference configuration was at
, the rate of change of temperature of the
material particle which in the reference configuration was at 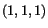 .
.
Solution
(i) |
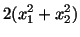 |
|
 |
![$\displaystyle 2 [X^2_1 (1 + t)^2 + X^2_2(1 + t)^2]$](img447.gif) |
|
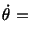 |
![$\displaystyle 2[2X^2_1(1 + t) + 2X^2_2(1 + t)]$](img449.gif) |
|
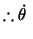 |
at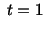 for the material particle for the material particle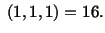 |
|
 |
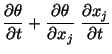 |
|
 |
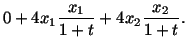 |
|
At 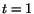 , for the material particle
, for the material particle 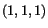
Exercise: The motion of a continuous medium is
defined by the equations
- (a)
- Express the velocity components in terms of
referential coordinates and time.
- (b)
- Express the velocity components in terms of spatial coordinates
and time.
Exercise: Given the motion of a body to be
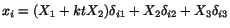 , and the temperature
field by
, and the temperature
field by
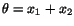 , find
, find
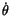 for the particle which
currently is at the place
for the particle which
currently is at the place 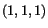 .
.
![]() .
.
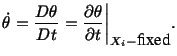
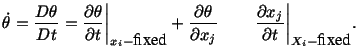
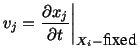
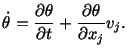
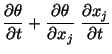
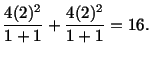
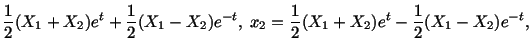
![]() , and the temperature
field by
, and the temperature
field by
![]() , find
, find
![]() for the particle which
currently is at the place
for the particle which
currently is at the place ![]() .
.